2020年发表文章
1. Zhu Fuping, Guo Xiang, Zhang Fumin*, Zhang Xiaoming, Wang Hong, Tu Yongqiang*. Construction of Polyfunctionalized 6−5−5 Fused Tricyclic Carbocycles via One-Pot Sequential Semipinacol Rearrangement/Michael Addition/Henry Reaction. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(5), 2076-2080. (https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00565) IF: 6.091
Abstract

A novel one-pot semipinacol rearrangement/Michael addition/Henry reaction of vinylogous α-ketols with nitroolefins has been achieved through the promotion of two Lewis acids, namely, TMSOTf and TiCl4, at temperatures between 0 and −78 °C. A range of synthetically challenging polyfunctionalized 6–5–5 and 7–5–5 fused tricyclic carbocycles bearing up to five continuous stereocenters, including one quaternary carbon center, are rapidly constructed in moderate to good yields with good to high diastereoselectivities in most cases.
2. Yang Jie, Zhang Xiaoming*, Zhang Fumin, Wang Shaohua, Tu Yongqiang*, Li Zhen, Wang Xichao, Wang Hong. Enantioselective Catalytic Aldehyde α-Alkylation/Semipinacol Rearrangement: Construction of α-Quaternary-δ-Carbonyl Cycloketones and Total Synthesis of (+)-Cerapicol. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(22), 8471-8475. (https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202001100) IF: 12.959
Abstract
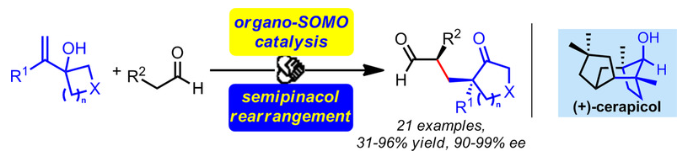
An enantioselective aldehyde α-alkylation/semipinacol rearrangement was achieved through organo-SOMO catalysis. The catalytically generated enamine radical cation serves as a carbon radical electrophile that can stereoselectively add to the alkene of an allylic alcohol and initiate ensuing ring-expansion of cyclopropanol or cyclobutanol. This tandem reaction enables the production of a wide range of nonracemic functionalizable α-quaternary-δ-carbonyl cycloketones in high yields and excellent enantioselectivity from simple aldehydes and allylic alcohols. As a key step, the intramolecular reaction was also successfully applied in the asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-cerapicol.
3. Wei Bin#, Wang Yakun#, Qiu Wenhui, Wang Sijia, Wu Yuehong, Xu Xuewei, Wang Hong*. Discovery and mechanism of intestinal bacteria in enzymatic cleavage of C–C glycosidic bonds. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104, 1883-1890. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10333-z) IF: 3.530
Abstract
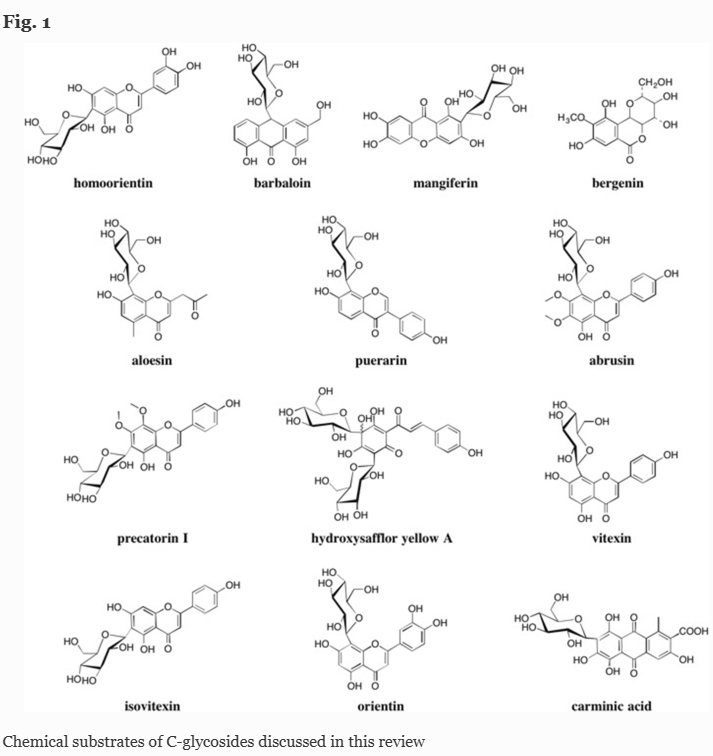
C-Glycosides, a special type of glycoside, are frequently distributed in many kinds of medicinal plants, such as puerarin and mangiferin, showing various and significant bioactivities. C-Glycosides are usually characterized by the C–C bond that forms between the anomeric carbon of sugar moieties and the carbon atom of aglycon, which is usually resistant against acidic hydrolysis and enzymatic treatments. Interestingly, C-glycosides could be cleaved by several intestinal bacteria, but whether the enzymatic cleavage of C–C glycosidic bond is reduction or hydrolysis has been controversial; furthermore, whether existence of a “C-glycosidase” directly catalyzing the cleavage is not clear. Here we review research advances about the discovery and mechanism of intestinal bacteria in enzymatic cleavage of C–C glycosidic bond with an emphasis on the identification of enzymes manipulation the deglycosylation. Finally, we give a brief conclusion about the mechanism of C-glycoside deglycosylation and perspectives for future study in this field.
4. Jin Weihua, Tang Hong, Zhang Jinmei, Wei Bin, Sun Jiadong, Zhang Wenjing, Zhang Fuming, Wang Hong, Robert J. Linhardt*, Zhong Weihong*. Structural analysis of a novel sulfated galacto-fuco-xylo-glucurono-mannan from Sargassum fusiforme and its anti-lung cancer activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020,149, 450-458. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.275) IF: 5.162
Abstract
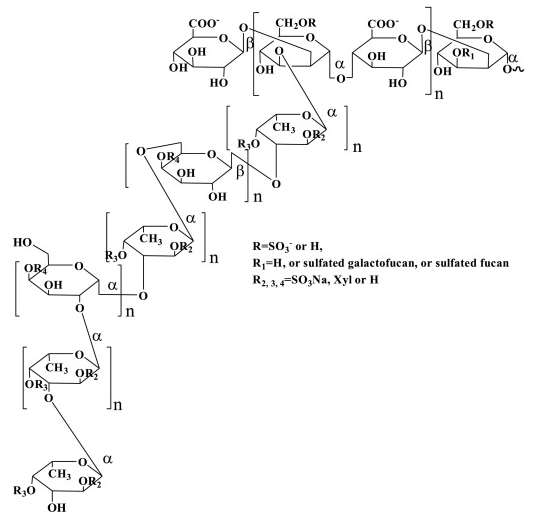
![]()
Polysaccharide (HFSGF) was purified from Sargassum fusiforme. Autohydrolysis and gel column chromatography were performed to fractionate HFSGF into three components (HFSGF-S, HFSGF-L and HFSGF-H). Compositional analysis, mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy were used to elucidate the structural features of HFSGF. HFSGF-S was a mixture of sulfated galacto-fuco-oligomers, from the branches terminal ends; in HFSGF-L, the branches of HFSGF, was a sulfated galactofucan, containing a backbone of 1,3-linked α-L-fucan sulfated at C2/4 and/or C4 and interspersed with galactose (Gal); and in HFSGF-H, the backbone of HFSGF, was composed of alternating 1,2-linked α-D-mannose (Man) and 1,4-linked β-D-glucuronic acid (GlcA), branched with sulfated galactofucan or sulfated fucan, 1,3-linked α-L-fucan sulfated at C2/4 and/or C4 and partly interspersed with Gal. Some fucose (Fuc) residues were also partially branched with xylose (Xyl). The anti-lung cancer activities of HFSGF-L and HFSGF-H against human lung cancer A549 cells in vitro and A549 xenograft tumor growth in vivo were determined. HFSGF-H had higher activity in vitro (IC50 ~12 mg/mL for 24 h) and in vivo (tumor inhibition ~51%.) than HFSGF-L, indicating that HFSGF-H might be a leading compound for a potential new therapeutics for the treatment of lung cancer.
5. Jin Weihua*, He Xinyue, Long Liufei, Fang Qiufei, Wei Bin, Sun Jiadong, Zhang Wenjing, Wang Hong, Zhang Fuming, Robert J. Linhardt. Structural characterization and anti-lung cancer activity of a sulfated glucurono-xylo-rhamnan from Enteromorpha prolifera. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 237, 116143-116152. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116143) IF: 7.182
Abstract
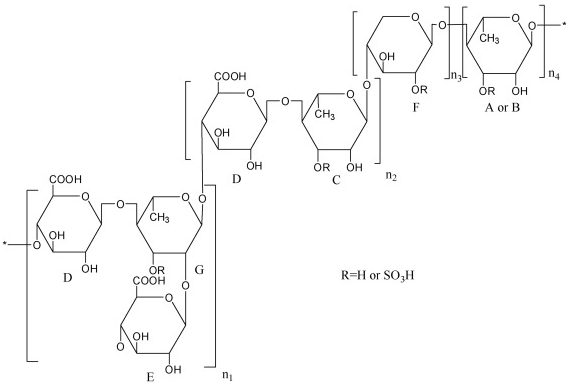
![]()
A sulfated glucurono-xylo-rhamnan (EP-3-H) was purified from a green alga, Enteromorpha prolifera. EP-3-H and its oligomers were characterized by high performance liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry and one and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resource spectroscopy. The structural analysis showed EP-3-H has a backbone of glucurono-xylo-rhamnan, branches with glucuronic acid and sulfated at C3 of rhamnose and/or C2 of xylose. The inhibition of EP-3-H on human lung cancer A549 cell proliferation in vitro and its therapeutic effects in BALB/c-nu mice in vivo were determined to evaluate the anti-lung cancer activity of EP-3-H. The tumor inhibition level was 59 %, suggesting that EP-3-H might be a good candidate for the treatment of lung cancer. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) studies revealed the IC50 on the binding of fibroblast growth factors, (FGF1 and FGF2), to heparin were 0.85 and 1.47 mg/mL, respectively. These results suggest that EP-3-H inhibits cancer proliferation by interacting with these growth factors.
6. Yin Jianhua#, Ren Wei#, Wei Bin#, Huang Huimin, Li Mingxing, Wu Xiaoxiao, Wang Anqi, Xiao Zhangang, Shen Jing, Zhao Yueshui, Du Fukuan, Ji Huijiao, Parham Jabbarzadeh Kaboli, Yongshun Ma, Zhang Zhuo, Cho Chi Hin, Wang Shengpeng*, Wu Xu*, Wang Yitao. Characterization of chemical composition and prebiotic effect of a dietary medicinal plant Penthorum Chinense Pursh. Food Chemistry, 2020, 319, 126568. ( DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126568) IF: 6.306
Abstract
![]()
Penthorum chinense Pursh is a dietary medicinal plant widely distributed in Asia-Pacific countries. The present study aims to profile the chemical constituents of P. chinense and investigate its prebiotic role in modulating gut microbiota. Fifty polyphenolic compounds were rapidly identified using UPLC-HR-MS. Total flavonoid and phenolic contents of P. chinense were 46.6% and 61.3% (w/w), respectively. Thirteen individual polyphenols were quantified, which accounted for 33.1% (w/w). P. chinense induced structural arrangement of microbial community in mice, showing increased microbiota diversity, elevated Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio and enriched gut health-promoting bacteria. After a one-week drug-free wash, most of these changes were recovered, but the abundance of some beneficial bacteria was further increased. The altered composition of gut microbiota enriched several metabolic pathways. Moreover, P. chinense increased antioxidant capacity in vivo. The results suggest that polyphenol-enriched P. chinense modulates gut microbiota and enhances antioxidant capacity in mice toward a beneficial environment for host health.
7. Wu Xiaoxiao#, Wang Shengpeng#, Li Mingxing#, Li Jing, Shen Jing, Zhao Yueshui, Pang Jun, Wen Qinglian, Chen Meijuan, Wei Bin, Parham Jabbarzadeh Kaboli, Du Fukuan, Zhao Qijie, Cho Chi Hin, Wang Yitao, Xiao Zhangang*, Wu Xu*. Conditional reprogramming: next generation cell culture. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2020, 8(10), 1360-1381. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.011) IF: 5.911
Abstract
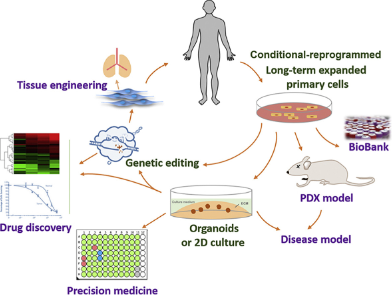
Long-term primary culture of mammalian cells has been always difficult due to unavoidable senescence. Conventional methods for generating immortalized cell lines usually require manipulation of genome which leads to change of important biological and genetic characteristics. Recently, conditional reprogramming (CR) emerges as a novel next generation tool for long-term culture of primary epithelium cells derived from almost all origins without alteration of genetic background of primary cells. CR co-cultures primary cells with inactivated mouse 3T3-J2 fibroblasts in the presence of RHO-related protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632, enabling primary cells to acquire stem-like characteristics while retain their ability to fully differentiate. With only a few years’ development, CR shows broad prospects in applications in varied areas including disease modeling, regenerative medicine, drug evaluation, drug discovery as well as precision medicine. This review is thus to comprehensively summarize and assess current progress in understanding mechanism of CR and its wide applications, highlighting the value of CR in both basic and translational researches and discussing the challenges faced with CR.
8. Bao Xiaoze*, Jean Rodriguez, Damien Bonne*. Enantioselective Synthesis of Atropisomers with Multiple Stereogenic Axes. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59 (31), 12623-12634. (https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202002518) IF: 12.959
Abstract
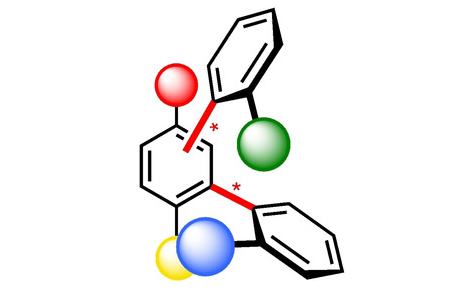
Atropisomers possessing multiple stereogenic axes are intriguing molecules with huge potential. However, only few approaches for their enantioselective synthesis are available due to the difficulties in assembling various stereogenic axes with high enantiocontrol. Only recently, innovative methods have emerged, opening new possibilities for the synthesis of this original class of atropisomeric compounds. This Minireview describes the development of this field based on a classification of the multi-axis systems according to the distance between the stereogenic axes and the strategy used to build them.
9. Chin. Kek Foo, Ye Xinyi*, Li Yongxin, Lee Richmond, Kabylda. Adil M, Leow D, Zhang Xin, Ang Esther Cai Xia, Tan Choon-Hong*. Bisguanidinium Catalyzed Epoxidation of Allylic and Homoallylic Amines under Phase Transfer Conditions. ACS Catal, 2020, 10, 2684-2691. (https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b04862) IF: 12.350
Abstract

A highly enantioselective epoxidation reaction of allylic and homoallylic amines has been disclosed using an ion pair catalyst, which consists of chiral cationic bisguanidinium [BG]2+ and an achiral tetraperoxyditungstate anion [W2O2(μ-O)(O2)4]2–. The terminal oxidant is a stoichiometric amount of aqueous hydrogen peroxide, an environmentally benign reagent. Up to 96% enantiomeric excess and 99% yields were achieved for 1,1′-disubstituted and 1,2-disubstituted allylic protected amines and 1,2-disubstituted homoallylic protected amines. The identity of the ion pair catalyst was uncovered using X-ray crystallography and revealed that the achiral tetraperoxyditungstate anion species [W2O2(μ-O)(O2)4]2– is nudged nicely into the central cavity of the chiral dication. The ion pair catalyst was also characterized using infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopies. The synthesis of (−)-venlafaxine was achieved via this reported methodology to demonstrate its usefulness.
10. Wu Qihao#, Li Songwei#, Xu Heng#, Wang Hong, Hu Pei, Zhang Hao, Luo Cheng, Chen Kaixian, Bastien Nay*, Guo Yuewei*, Li Xuwen*. Complex Polypropionates from a South China Sea Photosynthetic Mollusk: Isolation and Biomimetic Synthesis Highlighting Novel Rearrangements. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 132, 2-10. (https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202003643) IF: 12.959
Abstract
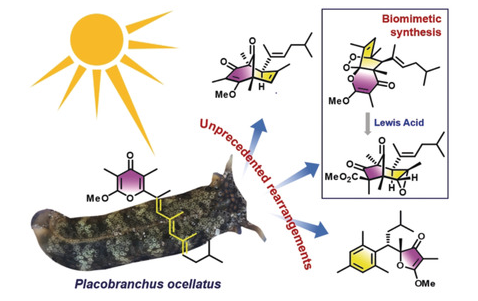
Placobranchus ocellatus is well known to produce diverse and complex γ-pyrone polypropionates. In this study, the chemical investigation of P. ocellatus from the South China Sea led to the discovery and identification of ocellatusones A–D, a series of racemic non-γ-pyrone polyketides with novel skeletons, characterized by a bicyclo[3.2.1]octane (1, 2), a bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane (3) or a mesitylene-substituted dimethylfuran-3(2H)-one core (4). Extensive spectroscopic analysis, quantum chemical computation, chemical synthesis, and/or X-ray diffraction analysis were used to determine the structure and absolute configuration of the new compounds, including each enantiomer of racemic compounds 1–4 after chiral HPLC resolution. An array of new and diversity-generating rearrangements is proposed to explain the biosynthesis of these unusual compounds based on careful structural analysis and comparison with six known co-occurring γ-pyrones (5–10). Furthermore, the successful biomimetic semisynthesis of ocellatusone A (1) confirmed the proposed rearrangement through an unprecedented acid induced cascade reaction.
11. Yin Fangzhou, Yang Min, Li Songwei, Wu Mengjun, Huan Xiajuan, Miu Zehong, Wang Hong*, Guo Yuewei*. Two new hydroperoxy steroids from the South China Sea goronian Rumphella sp. Steroids, 2020, 3 (155), 108558-108571. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108558) IF: 1.948
Abstract
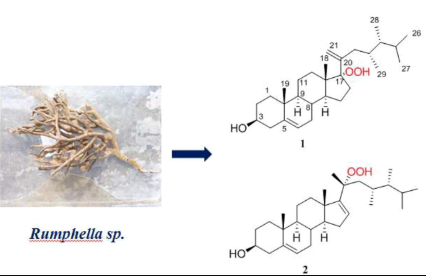
Two new hydroperoxy steroids, namely, xidaosteroids A and B (1 and 2), along with five known related compounds 3–7, were isolated from the South China Sea gorgonian Rumphella sp.. Their structures were established by extensive spectroscopic analyses and comparison of the spectral data with those reported in the literature. In bioassay, compound 3 showed weak cytotoxicities against SNU-398 and Capan-1 cells.
12. Chen Jun, Liu Pengfu, Chu Xiaohe, Zhang Huawei, David C. Rowley, Wang Hong*. Metabolic Pathway construction and optimization of Escherichia coli for high-Level ectoine production. Current Microbiology, 2020, 77, 1412-1418. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01888-6) IF: 1.746
Abstract
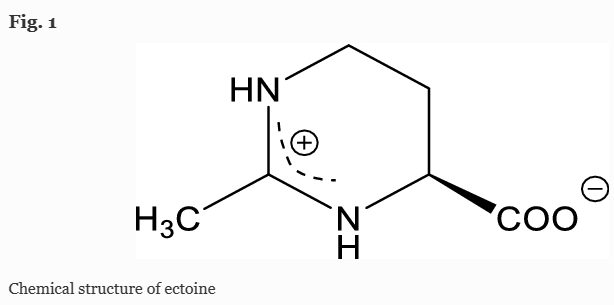
Ectoine is widely produced by various bacteria as a natural cell protectant against environment stress, e.g., osmotic and temperature stress. Its protective properties therefore exhibit high commercial value, especially in agriculture, medicine, cosmetics, and biotechnology. Here, we successfully constructed an engineered Escherichia coli for the heterologous production of ectoine. Firstly, the ectABC genes from Halomonas elongata were introduced into E. coli MG1655 to produce ectoine without high osmolarity. Subsequently, lysA gene was deleted to weaken the competitive L-lysine biosynthesis pathway and ectoine bioconversion was further optimized, leading to an increase of ectoine titer by 16.85-fold. Finally, at the low cell density of 5 OD600/mL in Erlenmeyer flask, the concentration of extracellular ectoine was increased to 3.05 mg/mL. At the high cell density of 15 OD600/mL, 12.7 g/L of ectoine was achieved in 24 h and the overall yield is 1.27 g/g glycerol and sodium aspartate. Our study herein provides a feasible and valuable biosynthesis pathway of ectoine with a potential for large-scale industrial production using simple and cheap feedstocks.
13. Ke Songze#, Wei Bin#, Zhou Taoshun, Qiu Wenhui, Wang Sijia, Chen Jun, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Jin Weihua*, Wang Hong*. Structural characterization and α‐glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of fucoidans extracted from Saccharina japonica. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2020, 17(7), e2000233-e2000244. (https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202000233) IF: 2.039
Abstract
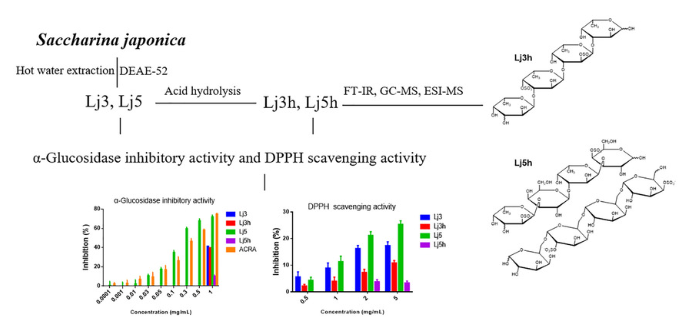
Two sulfated fucoidan fractions (Lj3 and Lj5) were extracted from Saccharina japonica and then subjected to acid hydrolysis to obtain Lj3h and Lj5h. Lj3h and Lj5h were characterized using IR, methylation analysis, and mass spectrometry. It was found that Lj3h and Lj5h were homogeneous low molecular weight fucoidans. Specifically, Lj3h was composed of the main chain of 1,3-linked α-L-fucopyranose residues with sulfate at C-2 and/or C-4 and three different monosaccharides (galactose, glucose, mannose) branched at C-2 and/or C-4 of fucose residue. Lj5h contained backbones of alternating galactopyranose residues and fucopyranose residues attached via a 1→3 linkage (galactofucan) and 1→6 linked galactan. The sulfation pattern was mainly located at C2/C4 fucose or galactose residues and more branches occupied at C-4 of fucose residue and C-2, C-3 or/and C-6 of galactose residue. In vitro assay indicated that, among the four fucoidans tested, only Lj5 showed potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 of 153.27±22.89 μg/mL, and the two parent fucoidans, Lj3 and Lj5, showed better antioxidant activity than their derivatives. These findings highlight the structure and bioactivity diversity of Saccharina japonica-derived fucoidans.
14. Hua Yi, Pan Rui, Bai Xuelian, Wei Bin, Chen Jianwei, Wang Hong*, Zhang Huawei*. Aromatic polyketides from a symbiotic strain Aspergillus fumigatus D and characterization of their biosynthetic gene D8.t287. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18 (6), 324. (https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/18/6/324) IF: 4.073
Abstract
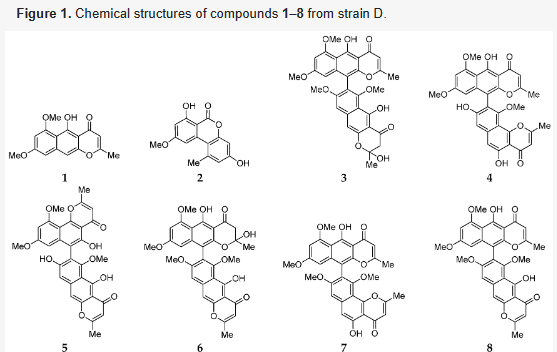
The chemical investigation of one symbiotic strain, Aspergillus fumigatus D, from the coastal plant Edgeworthia chrysantha Lindl led to the isolation of eight compounds (1–8), which were respectively identified as rubrofusarin B (1), alternariol 9-O-methyl ether (2), fonsecinone D (3), asperpyrone A (4), asperpyrone D (5), fonsecinone B (6), fonsecinone A (7), and aurasperone A (8) by a combination of spectroscopic methods (1D NMR and ESI-MS) as well as by comparison with the literature data. An antimicrobial assay showed that these aromatic polyketides exhibited no remarkable inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli, Staphyloccocus aureus and Candida albicans. The genomic feature of strain D was analyzed, as well as its biosynthetic gene clusters, using antibiotics and Secondary Metabolite Analysis Shell 5.1.2 (antiSMASH). Plausible biosynthetic pathways for dimeric naphtho-γ-pyrones 3–8 were first proposed in this work. A non-reducing polyketide synthase (PKS) gene D8.t287 responsible for the biosynthesis of these aromatic polyketides 1–8 was identified and characterized by target gene knockout experiment and UPLC-MS analysis.
15. Li Xingnuo, Hua Luxia, Zhou Taoshun, Wang Kebo, Wu Yuanyuan, Emam Mahmoud, Bao Xiaoze, Chen Jun, Wei Bin*. Cinnamic acid derivatives: inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase and structure-activity relationships. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 35(1), 1372-1378. (https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1780225) IF: 4.673
Abstract
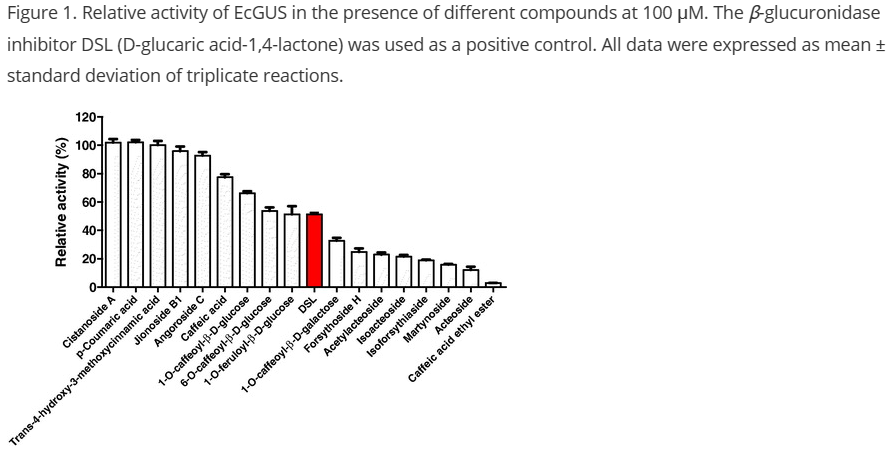
Gut microbial β-glucuronidase (GUS) is a potential therapeutic target to reduce gastrointestinal toxicity caused by irinotecan. In this study, the inhibitory effects of 17 natural cinnamic acid derivatives on Escherichia coli GUS (EcGUS) were characterised. Seven compounds, including caffeic acid ethyl ester (CAEE), had a stronger inhibitory effect (IC50 = 3.2–22.2 µM) on EcGUS than the positive control, D-glucaric acid-1,4-lactone. Inhibition kinetic analysis revealed that CAEE acted as a competitive inhibitor. The results of molecular docking analysis suggested that CAEE bound to the active site of EcGUS through interactions with Asp163, Tyr468, and Glu504. In addition, structure–activity relationship analysis revealed that the presence of a hydrogen atom at R1 and bulky groups at R9 in cinnamic acid derivatives was essential for EcGUS inhibition. These data are useful to design more potent cinnamic acid-type inhibitors of EcGUS.
16. Zhu Jinxin, Lu Yaojia, Chen Jun, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Bao Xiaoze, Ye Xinyi, Wang Hong*. Total synthesis of quinolactacin-H from marine-derived Penicillium sp. ENP701 and biological activities. RSC Advances, 2020,10, 24251-24254. (https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05244B) IF: 3.119
Abstract
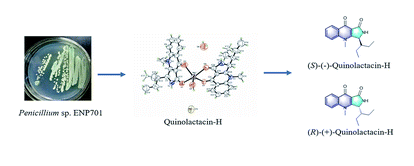
The quinolactacins are a family of pyrroloquinoline-type natural products from Penicillium sp. From the organic extract of Penicillium sp. ENP701 fermentation broth, a microorganism from the east China sea, one new quinolactacin was isolated and named quinolactacin-H. The structure of quinolactacin-H was determined by spectroscopic analysis and the absolute configurations by X-ray crystallographic analysis. Enantioselective total synthesis of (R)-(+)-quinolactacin-H and (S)-(−)-quinolactacin-H was achieved. When assayed through crystal violet (CV) microtiter plate biofilm, both (R) and (S)-quinolactacin-H showed a strong inhibition and dispersion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilms. Thus, quinolactacins could be proposed and developed as natural anti-bioflm agents in order to solve the problem of microbial resistance in future.
17. Chen Jianwei, Lu Yaojia, Ye Xinyi, Emam Mahmoud, Zhang Huawei, Wang Hong*. Current advances in Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing as drug discovery targets. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2020, 207, 112741.(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112741) IF: 5.573
Abstract
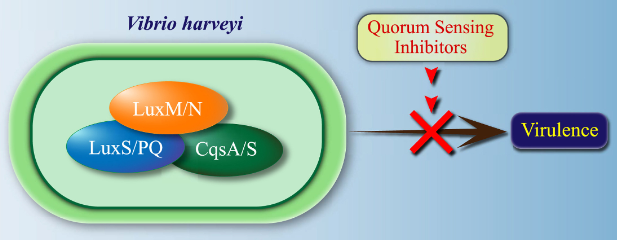
Vibrio harveyi is a marine bacterial pathogen which infects a wide range of marine organisms and results in severe loss. Antibiotics have been used for prophylaxis and treatment of V. harveyi infection. However, antibiotic resistance is a major public health threat to both human and animals. Therefore, there is an urgent need for novel antimicrobial agents with new modes of action. In V. harveyi, many virulence factors production and bioluminescence formation depend on its quorum sensing (QS) network. Therefore, the QS system has been widely investigated as an effective potential target for the treatment of V. harveyi infection. This perspective focuses on the quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) of V. harveyi QS systems (LuxM/N, LuxS/PQ, and CqsA/S) and evaluates medicinal chemistry strategies.
18. Chen Jianwei, Zhang Panqiao, Ye Xinyi, Wei Bin, Emam Mahmoud, Zhang Huawei, Wang Hong*. The structural diversity of marine microbial secondary metabolites based on co-culture strategy: 2009-2019. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18(9), 449. (https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090449) IF: 4.073
Abstract
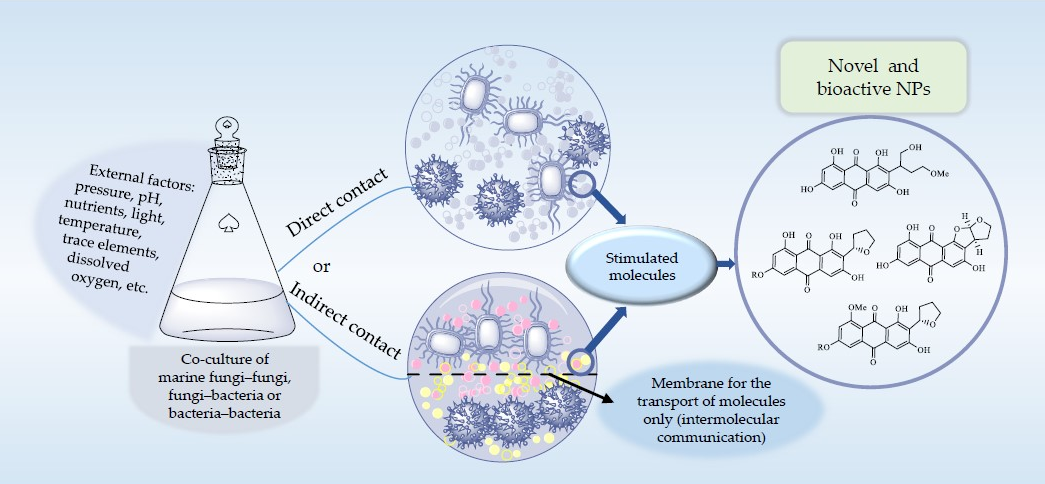
Marine microorganisms have drawn great attention as novel bioactive natural product sources, particularly in the drug discovery area. Using different strategies, marine microbes have the ability to produce a wide variety of molecules. One of these strategies is the co-culturing of marine microbes; if two or more microorganisms are aseptically cultured together in a solid or liquid medium in a certain environment, their competition or synergetic relationship can activate the silent biosynthetic genes to produce cryptic natural products which do not exist in monocultures of the partner microbes. In recent years, the co-cultivation strategy of marine microbes has made more novel natural products with various biological activities. This review focuses on the significant and excellent examples covering sources, types, structures and bioactivities of secondary metabolites based on co-cultures of marine-derived microorganisms from 2009 to 2019. A detailed discussion on future prospects and current challenges in the field of co-culture is also provided on behalf of the authors’ own views of development tendencies.
19. Wei Bin, Zhong Qiwu, Ke Songze, Zhou Taoshun, Xu Qiaoli, Wang Sijia, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Jin Weihua*, Hong Wang*. Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides prevent high-fat diet-induced early fasting hypoglycemia and regulate gut microbiota composition. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18(9), 444.(https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090444) IF: 4.073
Abstract
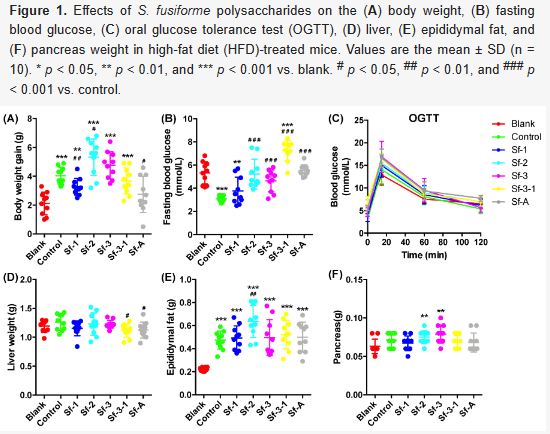
A low fasting blood glucose level is a common symptom in diabetes patients and can be induced by high-fat diet (HFD) feeding at an early stage, which may play important roles in the development of diabetes, but has received little attention. In this study, five polysaccharides were prepared from Sargassum fusiforme and their effects on HFD-induced fasting hypoglycemia and gut microbiota dysbiosis were investigated. The results indicated that C57BL/6J male mice fed an HFD for 4 weeks developed severe hypoglycemia and four Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides (SFPs), consisting of Sf-2, Sf-3, Sf-3-1, and Sf-A, significantly prevented early fasting hypoglycemia without inducing hyperglycemia. Sf-1 and Sf-A could also significantly prevent HFD-induced weight gain. Sf-2, Sf-3, Sf-3-1, and Sf-A mainly attenuated the HFD-induced decrease in Bacteroidetes, and all five SFPs had a considerable influence on the relative abundance of Oscillospira, Mucispirillum, and Clostridiales. Correlation analysis revealed that the fasting blood glucose level was associated with the relative abundance of Mucispinllum and Oscillospira. Receiver operating characteristic analysis indicated that Mucispinllum and Oscillospira exhibited good discriminatory power (AUC = 0.745–0.833) in the prediction of fasting hypoglycemia. Our findings highlight the novel application of SFPs (especially Sf-A) in glucose homeostasis and the potential roles of Mucispinllum and Oscillospira in the biological activity of SFPs.
20. Li Mingzhu, Yu Ronglu, Bai Xuelian, Wang Hong, Zhang Huawei*. Fusarium: a treasure trove of bioactive secondary metabolites. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(12), 1568-1588. (https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NP00038H) IF: 12.000
Abstract
Fusarium, one of the most common fungal genera, has received considerable attention because of its biosynthetic exuberance, the result of many unique gene clusters involved in the production of secondary metabolites. This review provides the first comprehensive analysis of the secondary metabolites unique to the genus Fusarium, describing their occurrence, bioactivity, and genome features.
21. Zhou Taoshun#, Wei Bin#, He Min#, Li Yasheng, Wang Yakun, Wang Sijia, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Cui Zining*, Wang Hong*. Thiazolidin-2-cyanamides derivatives as novel potent Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase inhibitors and their structure-inhibitory activity relationships. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 35(1), 1736-1742. (https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1816998) IF: 4.673
Abstract
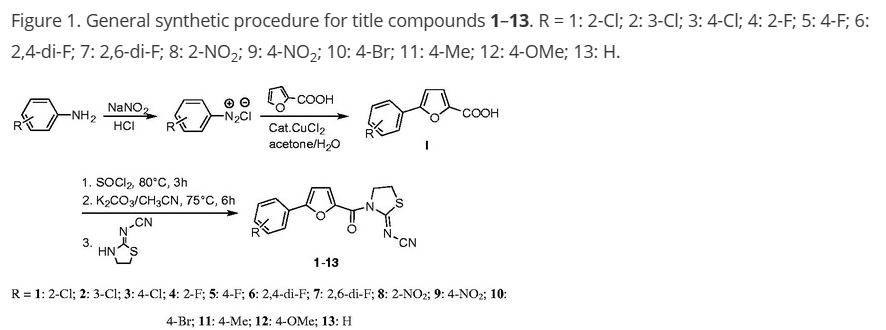
Gut microbial β-glucuronidases have the ability to deconjugate glucuronides of some drugs, thus have been considered as an important drug target to alleviate the drug metabolites-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. In this study, thiazolidin-2-cyanamide derivatives containing 5-phenyl-2-furan moiety (1–13) were evaluated for inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase (EcGUS). All of them showed more potent inhibition than a commonly used positive control, d-saccharic acid 1,4-lactone, with the IC50 values ranging from 1.2 µM to 23.1 µM. Inhibition kinetics studies indicated that compound 1–3 were competitive type inhibitors for EcGUS. Molecular docking studies were performed and predicted the potential molecular determinants for their potent inhibitory effects towards EcGUS. Structure–inhibitory activity relationship study revealed that chloro substitution on the phenyl moiety was essential for EcGUS inhibition, which would help researchers to design and develop more effective thiazolidin-2-cyanamide type inhibitors against EcGUS.
22. Wu Mengjun, Wang Hong*, Jiang Chengshi*, Guo Yuewei*. New cembrane-type diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinulariacrassa and their α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2020, 104, 104281. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104281) IF: 4.831
Abstract
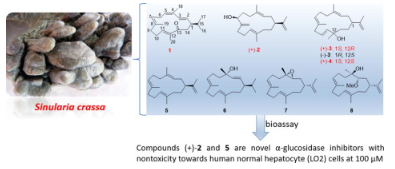
A detailed chemical research of the soft coral Sinularia crassa collected from the South China Sea yielded a series of cembrane-type diterpenoids, including four new cembranoids, namely sinulacrassins A − C (1, (+)-2, (+)-4) and ent-xishaflavalin G ((+)-3), along with five known analogs ((-)-3, 5–8). Their structures were elucidated by detailed spectroscopic analysis, chemical methods, and the comparison with those literature data. The absolute configuration of 1 was established by time-dependent density functional theory electronic circular dichroism (TDDFT/ECD) calculation, and the absolute configuration of (+)-2 was determined using the modified Mosher's method. The bioassay results revealed that (+)-2 and 5 were novel α-glucosidase inhibitors with IC50 values of 10.65 ± 0.16 and 30.31 ± 1.22 μM, respectively. In addition, (+)-2 and 5 were nontoxic towards human normal hepatocyte (LO2) cells at 100 μM. The present results highlighted the unusual coexistence of α and β configurations of C-1 in cembranoids from soft coral in the Order Alcyonacea, and provided new chemotype for the development of α-glucosidase inhibitors used in anti-diabetes treatment.
23. Bao Xiaoze*, Ren Jinhui, Yang Yang, Ye Xinyi, Wang Baomin, Wang Hong*. 2-Activated 1,3-enynes in enantioselective synthesis. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2020, 18(4), 7977-7986. (https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ob01614d) IF: 3.412
Abstract
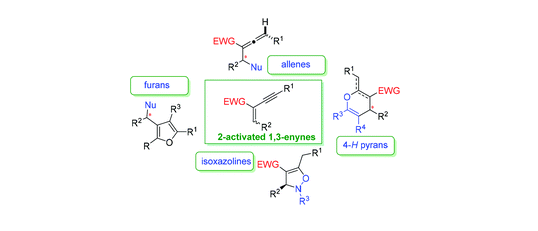
The rapid enantioselective synthesis of valuable building blocks and pharmaceutically important compounds from easily accessible precursors is one of the major areas of focus in organic chemistry. In this context, 2-activated 1,3-enyne has emerged as a powerful synthon in recent years for the efficient synthesis of enantioenriched furans, allenes, 4-H-pyrans, and 4-isoxazolines, which are privileged scaffolds in bioactive compounds and natural products. This review will cover the history of the development of 2-activated 1,3-enyne in enantioselective synthesis along with the corresponding mechanisms, which may motivate further development in this area to forge more complex and valuable molecules.
24. Yang Xue, Zhu Zhonghui, Ji Xia, Liu Zhaoming, Zhang Hua, Wei Bin*. Complete genome sequence of Micromonospora craniellae LHW63014T, a potential metal ion-chelating agent producer. Marine Genomics, 2020, 100830. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2020.100830) IF: 1.672
Abstract
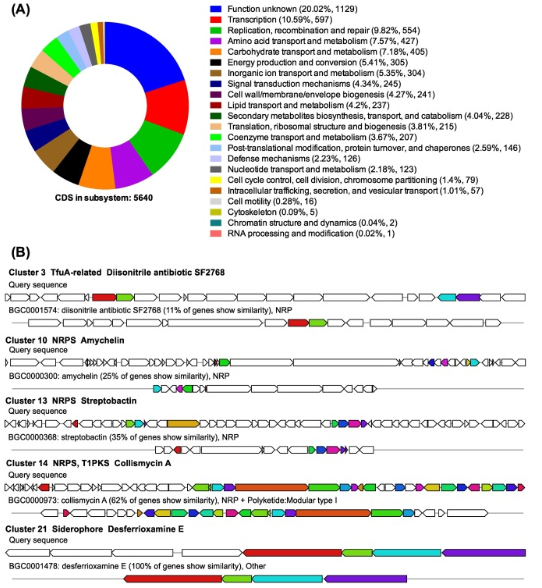

Micromonospora craniellae LHW63014T is a novel marine Micromonospora, isolated from a Craniella species sponge collected in the South China Sea. In this study, we report the complete genome sequence of M. craniellae LHW63014T, which is comprised of a circular chromosome of 6,839,926 bp with the G + C content of 70.9 mol%. The complete genome contained 6572 protein-coding genes, 48 tRNA genes, and 9 rRNA genes. Genomic annotations revealed that 79.09% of the protein-coding genes were assigned to the COG database, among which, the abundant genes were predicted to be involved in transcription, replication, recombination and repair, and amino acid transport and metabolism. Secondary metabolites prediction using antiSMASH revealed that 22 biosynthetic gene clusters (BGC) of secondary metabolites were located in the genome of M. craniellae LHW63014T, 19 of which showed low similarity (<50%) to known BGCs and 5 of which showed the closest homology with BGCs encoding metal ion-chelating agents, indicating the immense potential of M. craniellae LHW63014T to produce a wide variety of novel antibiotics, especially for metal ion-chelating agents.
25. Bao Xiaoze, Jean Rodriguez,* Damien Bonne*. Bidirectional enantioselective synthesis of bisbenzofuran atropisomeric oligoarenes featuring two distal C–C stereogenic axes. Chemical Science, 2020, 11, 403-408. (https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc04378k) IF: 9.346
Abstract
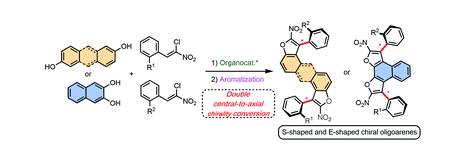
We report the bidirectional enantioselective synthesis of bis-benzofuran atropisomeric oligoarenes featuring two distal C–C stereogenic axes obtained by a two-fold central-to-axial chirality conversion upon oxidative aromatization. The key enantioenriched centrally chiral bis-dihydrobenzofuran precursors were synthesized via a bidirectional diastereo- and enantio-selective organocatalyzed domino reaction between simple achiral and easily accessible dihydroxylated aromatics and chloronitroalkenes. Moreover, the stereodivergent nature of the methodology was established by synthesizing both diastereomers of a non-symmetrically functionalized bis-axially chiral oligoarene.
26. Ye Xinyi, Peng ling, Bao Xiaoze, Choon-Hong Tan, Wang Hong*. Recent developments in highly efficient construction of P-stereogenic centers. Green Synthesis & Catalysis, 2020, 2, 6-18. (DOI:10.1016/j.gresc.2020.12.002)
Abstract
The construction of chiral phosphorus molecules with asymmetric center on the phosphorus atom has always been considered to be challenging in synthetic chemistry. Such P-stereogenic compounds possess many unique properties allowing many potential applications in natural products synthesis, pharmaceuticals as well as ligands in asymmetric organometallic catalysis. This increasing importance of P-stereogenic compounds has driven chemists to develop sophisticated strategies over the years to construct chiral phosphorus compounds. In this review, we aim to discuss the methodologies for the construction of P-stereogenic centers that were developed from 2005 to 2020. The review has been organized into seven sections according to their respective reaction principles beginning with desymmetrization, followed by phosphonoalkylation and phosphonoarylation, asymmetric addition, deprotonation, ring-closing metathesis, the use of organolithiums and Grignard reagents together with chiral auxiliaries and ending with kinetic resolution.
27. Wei Bin, Wang Yakun, Xiang Shoukui, Jiang Yan, Chen Rong, Hu Nan*. Alterations of gut microbiome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had undergone cholecystectomy. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2020. (https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00471.2020) IF: 3.469
Abstract
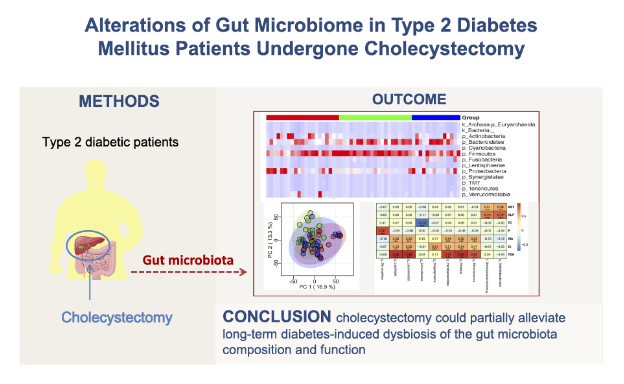
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have a high risk of developing cholecystic disease. The gut microbiota has been shownto be strongly associated with cholecystectomy and T2DM pathogenesis. However, alterations of the gut microbiome in patients withT2DM who had undergone cholecystectomy remain unexplored. In this study, the gut microbiomes of 14 long-term patients withT2DM who had undergone cholecystectomy (T2DIIC group) and 21 age- and/or sex-matched subjects with new-onset (T2DI group)and long-term (T2DII group) T2DM without cholecystectomy were assessed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing of stool samples. It wasfound that cholecystectomy could alleviate the decrease in Pielou’s evenness and the increase in the relative abundances of theFirmicutes phylum andLachnospiragenus in long-term patients with T2DM compared with T2DII subjects. Moreover, cholecystectomyalso significantly increased the relative abundance of the Fusobacteria phylum, as well as that of theFusobacteriumandBilophilagenera. Interestingly, the T2DIIC and T2DI groups showed higher similarities than the T2DII group with respect to patterns of gutmicrobiota composition and predicted gut metagenomes. In summary, cholecystectomy could partially alleviate long-term diabetes-induced dysbiosis of the gut microbiota composition and function, but alterations in T2DM patient health warrant further study.
28. Yin Fangzhou, Huan Xiajuan, I. Wayan Mudianta, Miao Zehong, Wang Hong*, Guo Yuewei*, Li Xuwen*. Polyoxygenated cembranoids from soft coral Lobophytum Crassum and their anti‐tumoral activities. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 39(3), 640-646. (https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202000539) IF:3.826
Abstract
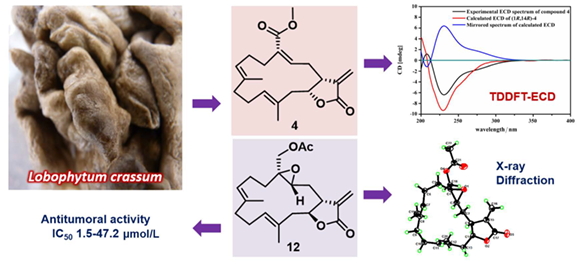
Four new cembranoids, 6-oxo-cembrene-A (1), lobocrassins G—H (2—3), and 14-epi-lobophytolide B (4), along with eight known related compounds (5—12), were isolated from the South China Sea soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Their structures were established by extensive spectroscopic analysis and by comparison of the spectral data with those reported in the literatures. The absolute stereochemistry of 14-epi-lobophytolide B (4) was established by time-dependent density functional theory electronic circular dichroism (TDDFT-ECD) calculations, whereas that of three known metabolites (6, 11 and 12) was also determined, for the first time, by using modified Mosher's method and/or X-ray diffraction analyses. In bioassay, the cembranoids 6, 7 and 12 showed significant anti-tumoral activity against A549, HT-29, SNU-398 and Capan-1 tumor cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 1.5 to 7.4 μmol/L. A preliminary structure-activity relationship was also discussed.

