2021年发表文章
1. Ye Xinyi*, Choon-Hong Tan*. Enantioselective transition metal catalysis directed by chiral cations. Chemical Science, 2021, 12, 533-539. (https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/SC/D0SC05734G#!divAbstract) IF: 9.346
Abstract
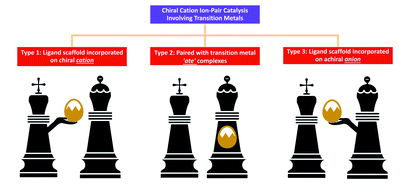
Enantioselective transition metal catalysis directed by chiral cations is the amalgamation of chiral cation catalysis and organometallic catalysis. Thus far, three strategies have been revealed: ligand scaffolds incorporated on chiral cations, chiral cations paired with transition metal ‘ate’-type complexes, and ligand scaffolds incorporated on achiral anions. Chiral cation ion-pair catalysis has been successfully applied to alkylation, cycloaddition, dihydroxylation, oxohydroxylation, sulfoxidation, epoxidation and C–H borylation. This development represents an effective approach to promote the cooperation between chiral cations and transition metals, increasing the versatility and capability of both these forms of catalysts. In this review, we present current examples of the three strategies and suggest possible inclusions for the future.
2. Li Yasheng#, Yang Xi#, Zhao Dongsheng#, Cai Yue, Huang Zhi, Wu Rui, Wang Sijia, Liu Guijun, Wang Jian, Bao Xiaoze, Ye Xinyi, Wei Bin, Cui Zining*, Wang Hong*. Design, synthesis and bioactivity study of 5-phenylfuran derivatives as potent reversal agents against P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in MCF7/ADR cell. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 113336. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0223523421001859) IF: 5.074
Abstract
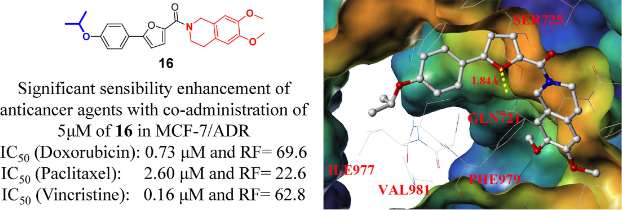
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) is a phenomenon in which cells become resistant to structurally and mechanistically unrelated drugs resulting in low intracellular drug concentrations. It is one of the noteworthy problems in malignant tumor clinical therapeutics. So P-gp protein is one of the ideal targets to solve MDR. Based on the lead compound 5m obtained from our previous work, a series of furan derivatives featuring alkyl-substituted phenols and 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline were designed and synthesized as reversal agents against P-gp in this paper. Compound 16 containing isopropoxy possessed good potency against P-gp mediated MDR in MCF-7/ADR (IC50 (doxorubicin) = 0.73 μM, RF = 69.6 with 5 μM 16 treated). Western blot results and Rh123 accumulation assays showed that 16 effectively inhibited P-gp efflux function but not its expression. The preliminary structure–activity relationship and docking studies demonstrated that compound 16 would be a potential P-gp inhibitor. Most worthy of mention is that compound 16 has achieved satisfactory results in combination with a variety of anti-tumor drugs, such as doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and vincristine. This study forwards a hopeful P-gp inhibitor for withstanding malignant tumor cell with multidrug resistance setting the basis for further studies.
3. Li Yasheng#, He Min#, Zhou Taoshun#, Wang Qin#, He Lulu, Wang Sijia, Hu Bei, Wei Bin*, Wang Hong*, Cui Zining*. 2,5-Disubstituted furan derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety as potent α-glucosidase and E. coli β-glucuronidase inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 216, 113322. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0223523421001719) IF: 5.074
Abstract
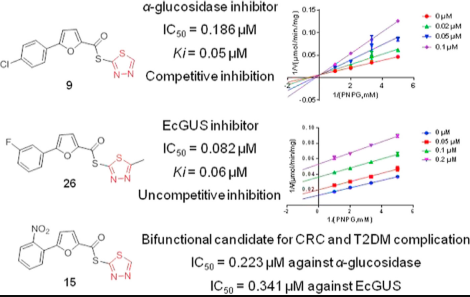
In this paper, the 2,5-disubstituted furan derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole were synthesized and screened for their inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and β-glucuronidases to obtain potent α-glucosidase inhibitor 9 (IC50 = 0.186 μM) and E. coli β-glucuronidase inhibitor 26 (IC50 = 0.082 μM), respectively. The mechanisms of the compounds were studied. The kinetic study revealed that compound 9 is a competitive inhibitor against α-glucosidase (Ki = 0.05 ± 0.003 μM) and molecular docking simulation showed several key interactions between 9 and the target including hydrogen bond and p-π stacking interaction. Derivative 26 (Ki = 0.06 ± 0.005 μM) displayed uncompetitive inhibition behavior against EcGUS. Furthermore, the result of docking revealed the furan ring of 26 may be a key moiety in obstructing the active domain of EcGUS. In addition, compound 15 exhibited significant inhibitory activity against these two enzymes, with potential therapeutic effects against diabetes and against CPT-11-induced diarrhea. At the same time, their low toxicity against normal liver tissue LO2 cells lays the foundation for in vivo studies and the development of bifunctional drug.
4. Zhang Jing, Yang Yang, Qian Xingkai, Song Peifang, Zhao Yishu, Guan Xiaoqing*, Zou Liwei*, Bao Xiaoze*, Wang Hong. Design, Synthesis, and Structure‐Activity Relationship Study of Pyrazolones as Potent Inhibitors of Pancreatic Lipase. ChemMedChem, 2021, 16, 1600. (https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202000850) IF: 3.050
Abstract
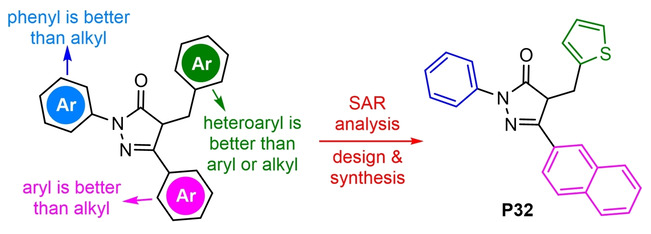
Pancreatic lipase (PL), a key target for the prevention and treatment of obesity, plays crucial roles in the hydrolysis and absorption of in dietary fat. In this study, a series of pyrazolones was synthesized, and their inhibitory effects against PL were assayed by using 4-methylumbelliferyl oleate (4-MUO) as optical substrate for PL. Comprehensive structure–activity relationship analysis of these pyrazolones led us to design and synthesize a novel compound P32 (5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-phenyl-4-(thiophen-2-ylmethyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one) as a potent mixed-competitive inhibitor of PL (IC50=0.30 μM). In addition, P32 displayed some selectivity over other known serine hydrolases. A molecular docking study for P32 demonstrated that the inhibitory activity of P32 towards PL could be attributed to the π-π interactions of 2-naphthyl unit (R1) and hydrophobic interactions of phenyl moiety (R3) with the active site of PL. Thus, P32 could serve as promising lead compound for the development of more efficacious and selective pyrazolones-type PL inhibitors for biomedical applications.
5. Wei Bin#, Wang Sijia#, Wang Yakun, Ke Songze, Jin Weihua, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Sun Jiadong, Henning Susanne M., Wang Jian*, Wang Hong*. Gut microbiota-mediated xanthine metabolism is associated with resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2021, 88, 108533. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108533) IF: 4.873
Abstract
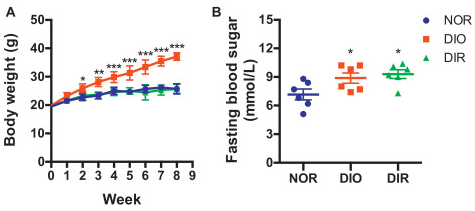

Resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity (DIR) has been observed in mice fed a high-fat diet and may provide a potential approach for anti-obesity drug discovery. However, the metabolic status, gut microbiota composition, and its associations with DIR are still unclear. Here, ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based urinary metabolomic and 16S rRNA gene sequencing-based fecal microbiome analyses were conducted to investigate the relationship between metabolic profile, gut microbiota composition, and body weight of C57BL/6J mice on chow or a high-fat diet for 8 weeks. PICRUSt analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences predicted the functional metagenomes of gut bacteria. The results demonstrated that feeding a high-fat diet increased body weight and fasting blood glucose of high-fat diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice and altered the host-microbial co-metabolism and gut microbiota composition. In DIR mice, high-fat diet did not increase body weight while fasting blood glucose was increased significantly compared to chow fed mice. In DIR mice, the urinary metabolic pattern was shifted to a distinct direction compared to DIO mice, which was mainly contributed by xanthine. Moreover, high-fat diet caused gut microbiota dysbiosis in both DIO and DIR mice, but in DIR mice, the abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae, Roseburia, and Escherichia was not affected compared to mice fed a chow diet, which played an important role in the pathway coverage of FormylTHF biosynthesis I. Meanwhile, xanthine and pathway coverage of FormylTHF biosynthesis I showed significant positive correlations with mouse body weight. These findings suggest that gut microbiota-mediated xanthine metabolism correlates with resistance to high-fat DIO.
6. Yang Yang#, Wang Xingyue#, Ye Xinyi, Wang Baomin, Bao Xiaoze*, Wang Hong*. Advances of α-activated cyclic isothiocyanate for the enantioselective construction of spirocycles. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2021, 19,4610. (https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/ob/d1ob00564b#!divAbstract) IF: 3.412
Abstract
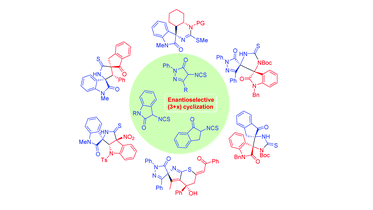
The efficient and enantioselective synthesis of pharmaceutically important spirocycles has attracted the focus of organic and medicinal chemists. In this context, with the excellent reactivity of α-activated isothiocyanate as formal 1,3-dipoles in the (3 + 2) cyclization process, the cyclic isothiocyanates featuring important pharmacophores, such as oxindole, pyrazolone, and indanone moieties, have emerged as powerful precursors to access a variety of spirocycles with highly structural diversities. In addition, the facile transformations of these spirocycles have shown potential applications in drug design. This review will cover the recent advances of α-activated cyclic isothiocyanates in the enantioselective construction of spirocycles since 2015, and the applications of corresponding products in organic and medicinal chemistry.
7. Yin Fangzhou, Yao Ligong, Zhang Zaiyong, Wang Jianrong, Wang Hong*, Guo Yuewei*. Polyoxygenated cembranoids from the Hainan Soft Coral Lobophytum crassum. Tetrahedron, 2021, 90,132204. (DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2021.132204) IF: 2.233
Abstract
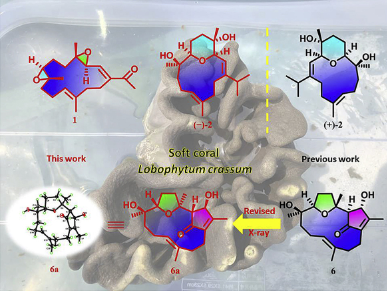
Five new uncommon cembranoids, named lobophycrasins A–D (1 and 3–5) and (−)-humilisin A (2), together with a known related one (6), have been isolated from Hainan soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis, NMR calculation with DP4+ probability analysis, TDDFT-ECD (time-dependent density functional theory-electronic circular dichroism) calculations and comparison with the reported data. Further, with the aid of X-ray diffraction analysis, the structure of lobocrasol (6), which was announced possessing novel unprecedented skeleton, was firmly revised as 6a. In addition, a plausible biogenetic connection among these isolates was also proposed.
8. Wu Mengjun, Liu Jiao, Wang Jianrong, Zhang Juan, Wang Hong*, Jiang Chengshi*, and Guo Yuewei*. Sinucrassins A—K, Casbane‐type Diterpenoids from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia crassa. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 39, 3367-3376. (DOI: 10.1002/cjoc.202100253) IF:3.826
Abstract
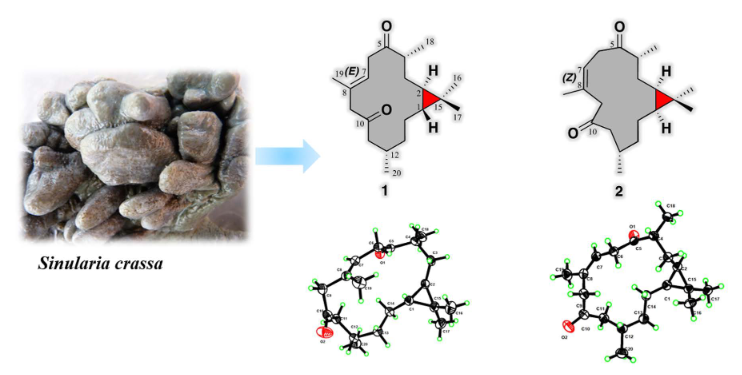
A detailed chemical study on the Hainan soft coral Sinularia crasshas resulted in the isolation and characterization of elevencas-bane-type diterpenoids, named sinucrassinsA—K(1—11), along with sixknown related ones (12—17). Their structures were eluci-dated by extensive spectroscopic analyses and comparison with the reported data. The absolute configurations of new compoundswere determined by the X-ray diffraction analysisandcomputer-assisted structural elucidation including 13C NMR data calculation and time-dependent density functional theory/electronic circular dichroism calculation.
9. Chen Wenchao, Choon-Hong Tan, Wang Hong*, Ye Xinyi*. The Development of Organocatalytic Asymmetric Reduction of Carbonyls and Imines Using Silicon Hydrides. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021,3091-3112. (https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ejoc.202100394) IF: 3.021
Abstract
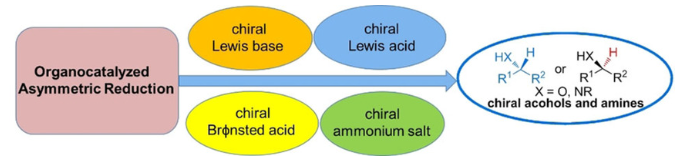
The asymmetric reduction of prochiral ketones and ketimines represents one of the most important and practical chemical transformations toward the synthesis of valuable chiral alcohols and amines. Among the existing strategies, organocatalyzed asymmetric reduction of carbonyls and imines using silicon hydrides is attractive due to low-cost, chemical stability, and easy handling in experiments. In this review, we wish to highlight the recent progress made in the past fifteen years in this field. Four catalytic systems of different activation modes are presented and discussed in detail. We aim to help shed light on common features that enable highly enantioselective silicon hydride reductions through organocatalysis and provide the design principles for the development of more effective catalytic systems.
10. Wei Bin#, Xu Qiaoli#, Zhang Bo, Zhou Taoshun, Ke Songze, Wang Sijia, Wu Bin, Xu Xuewei*, Wang Hong*. Comparative study of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides in regulating cecal and fecal microbiota of high-fat diet-fed mice. Marine Drugs, 2021, 19(7): 364. (https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070364) IF: 4.073
Abstract

Seaweed polysaccharides represent a kind of novel gut microbiota regulator. The advantages and disadvantages of using cecal and fecal microbiota to represent gut microbiota have been discussed, but the regulatory effects of seaweed polysaccharides on cecal and fecal microbiota, which would benefit the study of seaweed polysaccharide-based gut microbiota regulator, have not been compared. Here, the effects of two Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides prepared by water extraction (SfW) and acid extraction (SfA) on the cecal and fecal microbiota of high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice were investigated by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The results indicated that 16 weeks of HFD dramatically impaired the homeostasis of both the cecal and fecal microbiota, including the dominant phyla Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria, and genera Coriobacteriaceae, S24-7, and Ruminococcus, but did not affect the relative abundance of Firmicutes, Clostridiales, Oscillospira, and Ruminococcaceae in cecal microbiota and the Simpson’s index of fecal microbiota. Co-treatments with SfW and SfA exacerbated body weight gain and partially reversed HFD-induced alterations of Clostridiales and Ruminococcaceae. Moreover, the administration of SfW and SfA also altered the abundance of genes encoding monosaccharide-transporting ATPase, α-galactosidase, β-fructofuranosidase, and β-glucosidase with the latter showing more significant potency. Our findings revealed the difference of cecal and fecal microbiota in HFD-fed mice and demonstrated that SfW and SfA could more significantly regulate the cecal microbiota and lay important foundations for the study of seaweed polysaccharide-based gut microbiota regulators.
11. Li Yasheng#, Mao Shen#, Zhao Dongsheng#, Wang Cancan, Zu Dan, Yang Xi, Liu Guijun, Wang Sijia, Zhang Bo, Bao Xiaoze, Ye Xinyi, Wei Bin, Cui Zining*, Chen Jianwei*, Wang Hong*. Rational design of phenyl thiophene (pyridine) derivatives that overcome P-glycoprotein mediated MDR in MCF-7/ADR cell. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2021, 114, 105075. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105075) IF: 5.275
Abstract
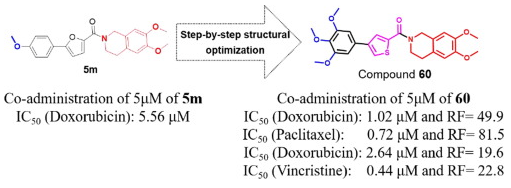
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) has become an important hindrance in the clinical treatment of malignant tumors. In this paper, based on our lead compound 5m and strategies of bioisosteric replacement and alkoxy effect, phenylthiophene and phenylpyridine derivatives were designed as chemosensitizers for front-line antineoplastic agents and overcomes P-gp mediated MDR in MCF-7/ADR cell. Generally, 4-phenylthiophene-2-carboxamide derivative 60 has been screened and obtained with optimal activity against P-gp mediated MDR in MCF-7/ADR (IC50 (doxorubicin) = 1.02 μM, RF = 49.9 with 5 μM 60 treated). The results of western blot and Rh123 accumulation assays showed that 60 effectively inhibited P-gp efflux function but not its expression. It is noted that compound 60 is a potentially broad-spectrum chemosensitizer in combination with commonly used anti-tumor drugs, such as doxorubicin, paclitaxel, daunorubicin and vincristine with RF value of 20–80.
12. Chen Wenchao, Choon-Hong Tan, Wang Hong*, Ye Xinyi*. Molybdenum/Tungsten-Based Heteropoly Salts in Oxidations.Chemistry- An Asian Journal, 2021, 16, 2753–277. (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asia.202100686) IF: 4.568
Abstract
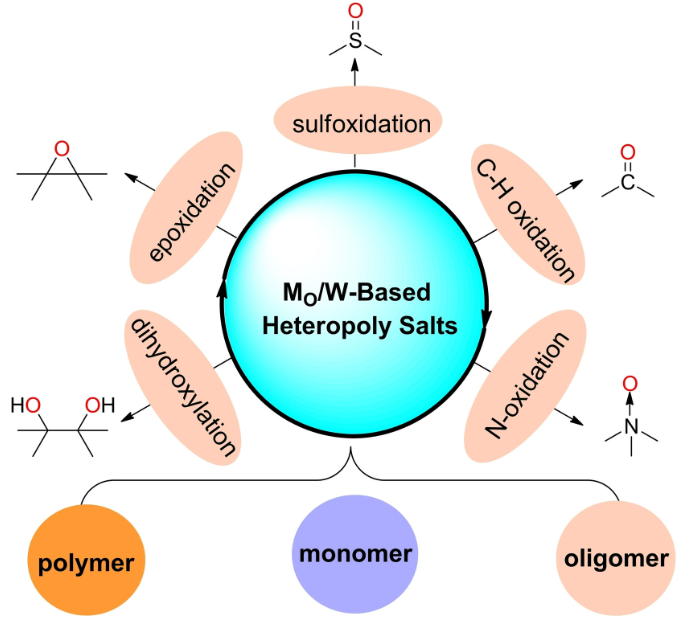
Oxidation represents one of the most important and practical chemical transformations for both organic synthesis, material science and pharmaceutical area. Among the existing strategies, molybdenum/tungsten-based heteropoly salts involved oxidations with low-cost and environmentally benign terminal oxidant and thus have attracted considerable attention in recent years. In this review, we have summarized the recent development of heteropoly salts utilized in oxidations, mainly the peroxomolybdates and peroxotungstates. We wish to highlight the progress made in the past 20 years of this field. Three categories are classified according to the aggregation state of metal oxides. Special attention is paid to the catalytically active peroxometalate species generated during the oxidation process. It is helpful to shed light on the common features that enable highly efficient and selective oxidations. We aim to inspire fellow chemists to explore more functional metalates for catalytic oxidations, especially asymmetric versions. Meanwhile, we attempt to understand the design principles for the discovery of more efficient, selective and economical catalytic systems.
13. Zhou Taoshun#, He Lulu#, He Jing, Yang Zhikun, Zhou Zhenyi, Du Aoqi, Yu Jinbiao, Li Yasheng, Wang Sijia, Wei Bin*, Cui Zining*, Wang Hong*. Discovery of a series of 5-phenyl-2-furan derivatives containing 1,3-thiazole moiety as potent Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2021, 105306. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045206821006830) IF: 5.275
Abstract
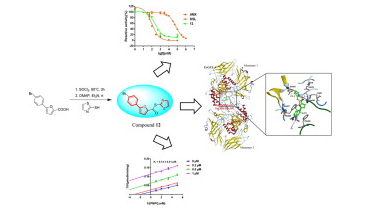
Gut microbial β-glucuronidases have drawn much attention due to their role as a potential therapeutic target to alleviate some drugs or their metabolites-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. In this study, fifteen 5-phenyl-2-furan derivatives containing 1,3-thiazole moiety (1–15) were synthesized and evaluated for their inhibitory effects against Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase (EcGUS). Twelve of them showed satisfactory inhibition against EcGUS with IC50 values ranging from 0.25 μM to 2.13 μM with compound 12 exhibited the best inhibition. Inhibition kinetics studies indicated that compound 12 (Ki = 0.14 ± 0.01 μM) was an uncompetitive inhibitor for EcGUS and molecular docking simulation further predicted the binding model and capability of compound 12 with EcGUS. A preliminary structure-inhibitory activity relationship study revealed that the heterocyclic backbone and bromine substitution of benzene may be essential for inhibition against EcGUS. The compounds have the potential to be applied in drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity and the findings would help researchers to design and develop more effective 5-phenyl-2-furan type EcGUS inhibitors.
14. Wei Bin#, Wang Yakun#,Yu Jinbiao, Wang Sijia, Yu Yanlei, Xu Xuewei*, Wang Hong*. Discovery of novel glycoside hydrolases from C-glycoside-degrading bacteria using sequence similarity network analysis. Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 59, 931–940 (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12275-021-1292-4) IF: 3.422.
Abstract
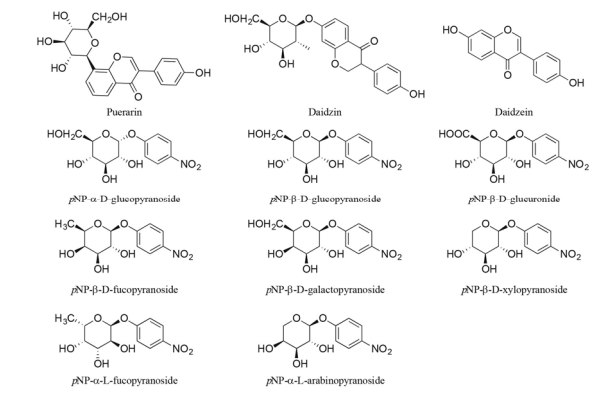
C-Glycosides are an important type of natural product with significant bioactivities, and the C-glycosidic bonds of C-glycosides can be cleaved by several intestinal bacteria, as exemplified by the human faeces-derived puerarin-degrading bacterium Dorea strain PUE. However, glycoside hydrolases in these bacteria, which may be involved in the C-glycosidic bond cleavage of C-glycosides, remain largely unknown. In this study, the genomes of the closest phylogenetic neighbours of five puerarin-degrading intestinal bacteria (including Dorea strain PUE) were retrieved, and the protein-coding genes in the genomes were subjected to sequence similarity network (SSN) analysis. Only four clusters of genes were annotated as glycoside hydrolases and observed in the genome of D. longicatena DSM 13814T (the closest phylogenetic neighbour of Dorea strain PUE); therefore, genes from D. longicatena DSM 13814T belonging to these clusters were selected to overexpress recombinant proteins (CG1, CG2, CG3, and CG4) in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). In vitro assays indicated that CG4 efficiently cleaved the O-glycosidic bond of daidzin and showed moderate β-D-glucosidase and β-D-xylosidase activity. CG2 showed weak activity in hydrolyzing daidzin and pNP-β-D-fucopyranoside, while CG3 was identified as a highly selective and efficient α-glycosidase. Interestingly, CG3 and CG4 could be selectively inhibited by daidzein, explaining their different performance in kinetic studies. Molecular docking studies predicted the molecular determinants of CG2, CG3, and CG4 in substrate selectivity and inhibition propensity. The present study identified three novel and distinctive glycoside hydrolases, highlighting the potential of SSN in the discovery of novel enzymes from genomic data.
15. Ke Songze#, Yu Yanlei#, Xu Qiaoli, Zhang Bo, Wang Sijia, Jin Weihua, Wei Bin*, Wang Hong*. Composition-activity relationships of polysaccharides from Saccharina japonica in regulating gut microbiota in short-term high-fat diet-fed mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(37):11121-11130. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04490) IF: 5.279.
Abstract

Saccharina japonica polysaccharide could modulate gut microbiota composition; however, the composition-activity relationship remains unclear, thus restricting its application. In the current study, we investigated the impact of eight different S. japonica polysaccharide fractions on the gut microbiota after day 2 and day 14 treatments on high-fat diet (HFD) feeding mice. The results showed that a 2 day HFD dramatically altered gut microbiota composition, and the additional 12 day HFD further strengthened the gut microbiota dysbiosis in the HFD group. LjA-1 and LjA-3 could partially alleviate the dysbiosis of gut microbiota composition and significantly alter gut microbiota function. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that the sulfate content and the molecular weight distributions were the main factors affecting the dominant gut bacterial genera. Our findings reveal that gut microbiota homeostasis could be disordered by HFD at day 2 and provide insights into the quantitative composition-activity relationships of polysaccharides in regulating gut microbiota.
16. Wei Bin#, Du Aoqi#, Zhou Zhenyi, Lai Cong,Yu Wenchao, Yu Jinbiao, Yu Yanlei, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Xu Xuewei*, Wang Hong*. An atlas of bacterial secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters. Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 23(11):6981-6992. (DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.15761) IF: 5.491
Abstract
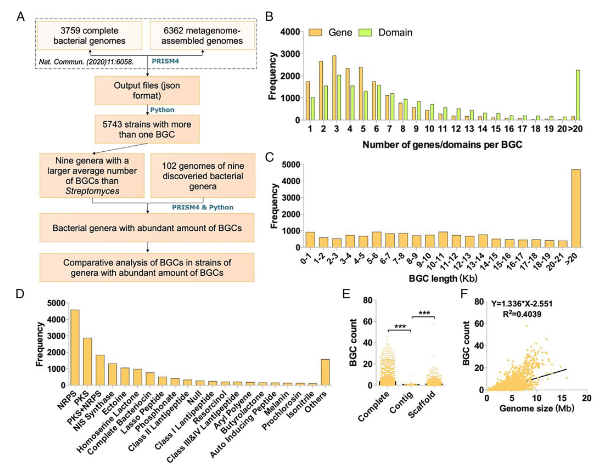
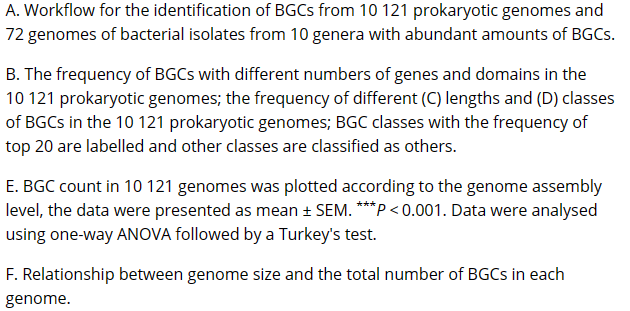
Bacterial secondary metabolites are rich sources of novel drug leads. The diversity of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) in genome-sequenced bacteria, which will provide crucial information for the efficient discovery of novel natural products, has not been systematically investigated. Here, the distribution and genetic diversity of BGCs in 10 121 prokaryotic genomes (across 68 phyla) were obtained from their PRISM4 outputs using a custom python script. A total of 18 043 BGCs are detected from 5743 genomes with non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (25.4%) and polyketides (15.9%) as the dominant classes of BGCs. Bacterial strains harbouring the largest number of BGCs are revealed and BGC count in strains of some genera vary greatly, suggesting the necessity of individually evaluating the secondary metabolism potential. Additional analysis against 102 strains of discovered bacterial genera with abundant amounts of BGCs confirms that Kutzneria, Kibdelosporangium, Moorea, Saccharothrix, Cystobacter, Archangium, Actinosynnema, Kitasatospora, and Nocardia, may also be important sources of natural products and worthy of priority investigation. Comparative analysis of BGCs within these genera indicates the great diversity and novelty of the BGCs. This study presents an atlas of bacterial secondary metabolite BGCs that provides a lot of key information for the targeted discovery of novel natural products.
17. Han Xue, Shan Lixin, Zhu Jinxin, Zhang Changsheng, Zhang Xiaoming, Zhang Fumin*, Wang Hong, Tu Yongqiang*, Yang Ming, Zhang Wenshuo. Copper-Nitrene-Catalyzed Desymmetric Oxaziridination/1,2-AlkylRearrangement of 1,3-Diketones toward Bicyclic Lactams. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 133, 1-6. (https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202107909) IF: 12.959
Abstract
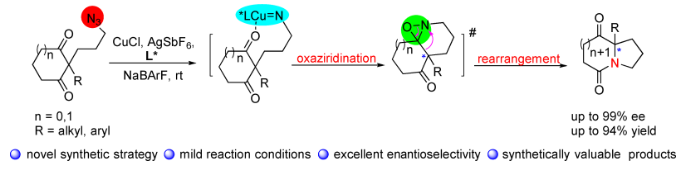
Although copper-nitrene has been extensively studied as a versatile active species in various transformations, asymmetric reactions involving copper-nitrene have been limited to the aziridination of olefins. Herein, we report the novel copper-nitrene-catalyzed desymmetric oxaziridination reaction of cyclic diketones with alkyl azides and the subsequent rearrangement of the resulting highly active intermediate, which produces a synthetically challenging chiral bicyclic lactam containing a quaternary carbon center. This procedure not only enriches the copper-nitrene-catalyzed asymmetric reactions, but also provides an alternative strategy to address the inherent challenges of catalytic asymmetric Schmidt reactions. This unique reaction could inspire the investigation of novel copper-nitrene-catalyzed asymmetric transformations and their reaction mechanisms.
18. Zeng Zirong, Li Wangsheng, Nay Bastien, Hu Pei, Zhang Haiyan*, Wang Hong*, Li Xuwen*, Guo Yuewei*. Sinunanolobatone A, an Anti-inflammatory Diterpenoid with Bicyclo[13.1.0]pentadecane Carbon Scaffold, and Related Casbanes from the Sanya Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Organic Letters, 2021, 23, 19, 7575-7579. (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c02772) IF:6.005
Abstract

A novel diterpenoid, sinunanolobatone A (1), featuring an unprecedented bicyclo[13.1.0]pentadecane carbon framework, along with two new casbane diterpenoids (2 and 3), and five known related ones (4–8) were isolated from the Sanya soft coral Sinularia nanolobata. The structures of the new compounds were established by detailed spectroscopic analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis, chemical reactions, or a quantum chemical computation method. A plausible biosynthetic pathway of 1 was proposed. In bioassay, the novel compound 1 showed significant inhibitory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced inflammation in BV-2 microglial cells.
19. Lin Na, Li Heng, Wang Jianrong , Tang Wei, Zheng Mingyue, Wang Hong*, Jiang Chengshi* and Guo Yuewei*. New Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2021, Accepted. (http://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202100597) IF: 6.000
Abstract
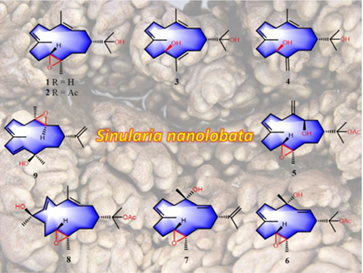
In the present study, nine new cembrane-type diterpenoids, namely ximaonanolobatins A—I (1—9), together with six related known analogs (10—15) and four known tetraprenylated alkaloids malonganenones D, E, H, and K (16—19) were isolated from the soft coral Sinularia nanolobata collected off the Ximao Island in the South China Sea. The structures of 1—9 were robustly established by a combination of detailed spectroscopic analyses, chemical reactions, quantum mechanical (QM)-NMR methods, biogenetic consideration, and the comparison with those literature data. The absolute configuration of 1 was confirmed by X-ray diffraction analysis, and the absolute configuration of 2 was determined by QM-NMR calculations and chemical transformation. In addition, the absolute configuration of 3 was determined using the modified Mosher's method. All these isolates were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activities. The results showed that only compound 15 exhibited potential anti-inflammatory effect against LPS-induced TNF-α release in RAW264.7 macrophages with an IC50 value of 12.6 μmol/L.
20. Chen Jinyun, Lv Sunyan, Liu Jia , Yu Yanlei, Wang Hong, Zhang Huawei*. An overview of bioactive 1,3-oxazole-containing alkaloids from marine organisms. Pharmaceutical, 2021, 14, 1274. (https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/14/12/1274) IF: 5.863
Abstract
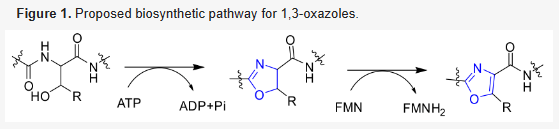
1,3-Oxazole chemicals are a unique class of five-membered monocyclic heteroarenes, containing a nitrogen atom and an oxygen. These alkaloids have attracted extensive attention from medicinal chemists and pharmacologists owing to their diverse arrays of chemical structures and biological activities, and a series of 1,3-oxazole derivatives has been developed into therapeutic agents (e.g., almoxatone, befloxatone, cabotegravir, delpazolid, fenpipalone, haloxazolam, inavolisib). A growing amount of evidence indicates that marine organisms are one of important sources of 1,3-oxazole-containing alkaloids. To improve our knowledge regarding these marine-derived substances, as many as 285 compounds are summarized in this review, which, for the first time, highlights their sources, structural features and biological properties, as well as their biosynthesis and chemical synthesis. Perspective for the future discovery of new 1,3-oxazole compounds from marine organisms is also provided.
21. Wu Wentao, Wang Hong*, Chen Jun, Bao Xiaoze*, Tan Choon-Hong, Ye Xinyi*. Dicyanopyrazine Derived Chromophore as An Efficient Photocatalyst for α-amino C-H Bond Functionalization. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021,10, 2876-2879. (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ajoc.202100467) IF: 3.319
Abstract
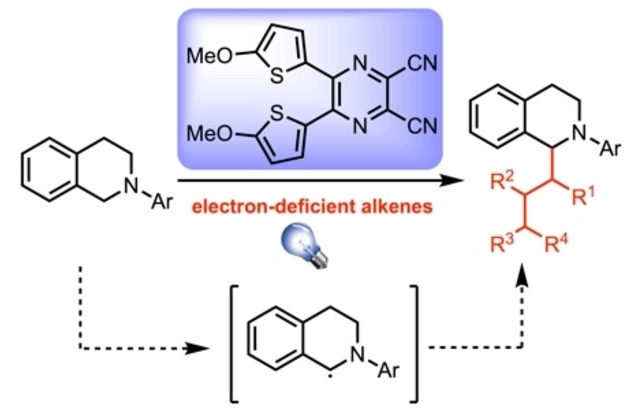
A formal method for C−H bond functionalization of amines with Michael acceptors and β-fluorinated gem-diols via α-aminoalkyl radicals generated using organic photoredox catalysis is reported. Under transition-metal free conditions, the α-aminoalkyl radicals are produced by dicyanopyrazine-derived photocatalyst through single electron transfer and subsequent deprotonation of C−H bonds, then the functionalized products are formed through later addition of generated radicals to electron-deficient alkenes. This work demonstrates the synthetic utilization of α-aminoalkyl radicals and photoredox potential of dicyanopyrazine-derived chromophore as a photocatalyst.
22. Zhong Qiwu, Zhou Taoshun, Qiu Wenhui, Wang Yakun, Xu Qiaoli, Ke Songze, Wang Sijia, Jin Weihua, Chen Jianwei, Zhang Huawei, Wei Bin*, Wang Hong*. Characterization and hypoglycemic effects of sulfated polysaccharides derived from brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chemistry, 2021, 341, 128148. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128148) IF: 7.514, 入选ESI高被引论文
Abstract
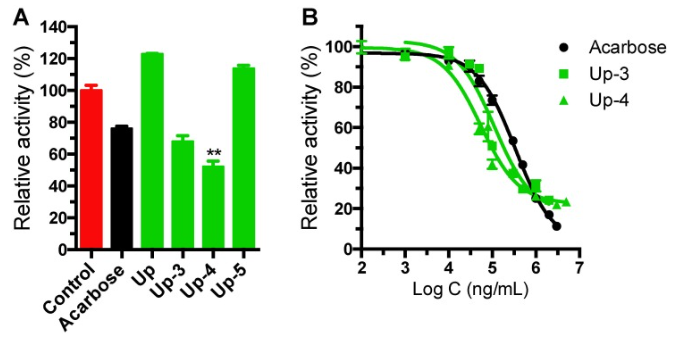
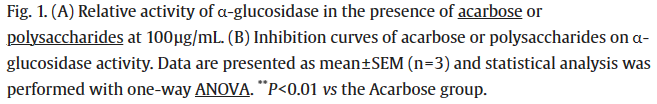
The brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharides show various biological activities, but their hypoglycemic activity and the underlying mechanism remain unclear. Here, three fractions of sulfated polysaccharides Up-3, Up-4, and Up-5 were prepared by microwave-assisted extraction from U. pinnatifida. In vitro assays demonstrated that Up-3 and Up-4 had strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, and Up-3, Up-4, and Up-5 could improve the glucose uptake in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells without affecting their viability. In vivo studies indicated Up-3 and Up-4 markedly reduced postprandial blood glucose levels. Up-U (a mixture of Up-3, Up-4, and Up-5), reduced fasting blood glucose levels, increased glucose tolerance and alleviated insulin resistance in HFD/STZ-induced hyperglycemic mice. Histopathological observation and hepatic glycogen measurement showed that Up-U alleviated the damage of the pancreas islet cell, reduced hepatic steatosis, and promoted hepatic glycogen synthesis. These findings suggest that Up-U could alleviate postprandial and HFD/STZ-induced hyperglycemia and was a potential agent for diabetes treatment.

